1# Sonic
2
3English | [中文](README_ZH_CN.md)
4
5A blazingly fast JSON serializing & deserializing library, accelerated by JIT (just-in-time compiling) and SIMD (single-instruction-multiple-data).
6
7## Requirement
8
9- Go 1.16~1.22
10- Linux / MacOS / Windows(need go1.17 above)
11- Amd64 ARCH
12
13## Features
14
15- Runtime object binding without code generation
16- Complete APIs for JSON value manipulation
17- Fast, fast, fast!
18
19## APIs
20
21see [go.dev](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/bytedance/sonic)
22
23## Benchmarks
24
25For **all sizes** of json and **all scenarios** of usage, **Sonic performs best**.
26
27- [Medium](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/decoder/testdata_test.go#L19) (13KB, 300+ key, 6 layers)
28
29```powershell
30goversion: 1.17.1
31goos: darwin
32goarch: amd64
33cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-9880H CPU @ 2.30GHz
34BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic-16 32393 ns/op 402.40 MB/s 11965 B/op 4 allocs/op
35BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 21668 ns/op 601.57 MB/s 10940 B/op 4 allocs/op
36BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 42168 ns/op 309.12 MB/s 14345 B/op 115 allocs/op
37BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_GoJson-16 65189 ns/op 199.96 MB/s 23261 B/op 16 allocs/op
38BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_StdLib-16 106322 ns/op 122.60 MB/s 49136 B/op 789 allocs/op
39BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic-16 6269 ns/op 2079.26 MB/s 14173 B/op 4 allocs/op
40BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 5281 ns/op 2468.16 MB/s 12322 B/op 4 allocs/op
41BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 20056 ns/op 649.93 MB/s 9488 B/op 2 allocs/op
42BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_GoJson-16 8311 ns/op 1568.32 MB/s 9481 B/op 1 allocs/op
43BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_StdLib-16 16448 ns/op 792.52 MB/s 9479 B/op 1 allocs/op
44BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 6681 ns/op 1950.93 MB/s 12738 B/op 4 allocs/op
45BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 4179 ns/op 3118.99 MB/s 10757 B/op 4 allocs/op
46BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 9861 ns/op 1321.84 MB/s 14362 B/op 115 allocs/op
47BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 18850 ns/op 691.52 MB/s 23278 B/op 16 allocs/op
48BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 45902 ns/op 283.97 MB/s 49174 B/op 789 allocs/op
49BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 1480 ns/op 8810.09 MB/s 13049 B/op 4 allocs/op
50BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 1209 ns/op 10785.23 MB/s 11546 B/op 4 allocs/op
51BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 6170 ns/op 2112.58 MB/s 9504 B/op 2 allocs/op
52BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 3321 ns/op 3925.52 MB/s 9496 B/op 1 allocs/op
53BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 3739 ns/op 3486.49 MB/s 9480 B/op 1 allocs/op
54
55BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic-16 66812 ns/op 195.10 MB/s 57602 B/op 723 allocs/op
56BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 54523 ns/op 239.07 MB/s 49786 B/op 313 allocs/op
57BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_StdLib-16 124260 ns/op 104.90 MB/s 50869 B/op 772 allocs/op
58BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 91274 ns/op 142.81 MB/s 55782 B/op 1068 allocs/op
59BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_GoJson-16 88569 ns/op 147.17 MB/s 66367 B/op 973 allocs/op
60BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic-16 32557 ns/op 400.38 MB/s 28302 B/op 137 allocs/op
61BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 28649 ns/op 455.00 MB/s 24999 B/op 34 allocs/op
62BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_StdLib-16 111437 ns/op 116.97 MB/s 10576 B/op 208 allocs/op
63BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 35090 ns/op 371.48 MB/s 14673 B/op 385 allocs/op
64BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_GoJson-16 28738 ns/op 453.59 MB/s 22039 B/op 49 allocs/op
65BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 12321 ns/op 1057.91 MB/s 57233 B/op 723 allocs/op
66BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 10644 ns/op 1224.64 MB/s 49362 B/op 313 allocs/op
67BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 57587 ns/op 226.35 MB/s 50874 B/op 772 allocs/op
68BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 38666 ns/op 337.12 MB/s 55789 B/op 1068 allocs/op
69BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 30259 ns/op 430.79 MB/s 66370 B/op 974 allocs/op
70BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 5965 ns/op 2185.28 MB/s 27747 B/op 137 allocs/op
71BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 5170 ns/op 2521.31 MB/s 24715 B/op 34 allocs/op
72BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 27582 ns/op 472.58 MB/s 10576 B/op 208 allocs/op
73BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 13571 ns/op 960.51 MB/s 14685 B/op 385 allocs/op
74BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 10031 ns/op 1299.51 MB/s 22111 B/op 49 allocs/op
75
76BenchmarkGetOne_Sonic-16 3276 ns/op 3975.78 MB/s 24 B/op 1 allocs/op
77BenchmarkGetOne_Gjson-16 9431 ns/op 1380.81 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
78BenchmarkGetOne_Jsoniter-16 51178 ns/op 254.46 MB/s 27936 B/op 647 allocs/op
79BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 216.7 ns/op 60098.95 MB/s 24 B/op 1 allocs/op
80BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Gjson-16 1076 ns/op 12098.62 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
81BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 17741 ns/op 734.06 MB/s 27945 B/op 647 allocs/op
82BenchmarkSetOne_Sonic-16 9571 ns/op 1360.61 MB/s 1584 B/op 17 allocs/op
83BenchmarkSetOne_Sjson-16 36456 ns/op 357.22 MB/s 52180 B/op 9 allocs/op
84BenchmarkSetOne_Jsoniter-16 79475 ns/op 163.86 MB/s 45862 B/op 964 allocs/op
85BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 850.9 ns/op 15305.31 MB/s 1584 B/op 17 allocs/op
86BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sjson-16 18194 ns/op 715.77 MB/s 52247 B/op 9 allocs/op
87BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 33560 ns/op 388.05 MB/s 45892 B/op 964 allocs/op
88BenchmarkLoadNode/LoadAll()-16 11384 ns/op 1143.93 MB/s 6307 B/op 25 allocs/op
89BenchmarkLoadNode_Parallel/LoadAll()-16 5493 ns/op 2370.68 MB/s 7145 B/op 25 allocs/op
90BenchmarkLoadNode/Interface()-16 17722 ns/op 734.85 MB/s 13323 B/op 88 allocs/op
91BenchmarkLoadNode_Parallel/Interface()-16 10330 ns/op 1260.70 MB/s 15178 B/op 88 allocs/op
92```
93
94- [Small](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/testdata/small.go) (400B, 11 keys, 3 layers)
95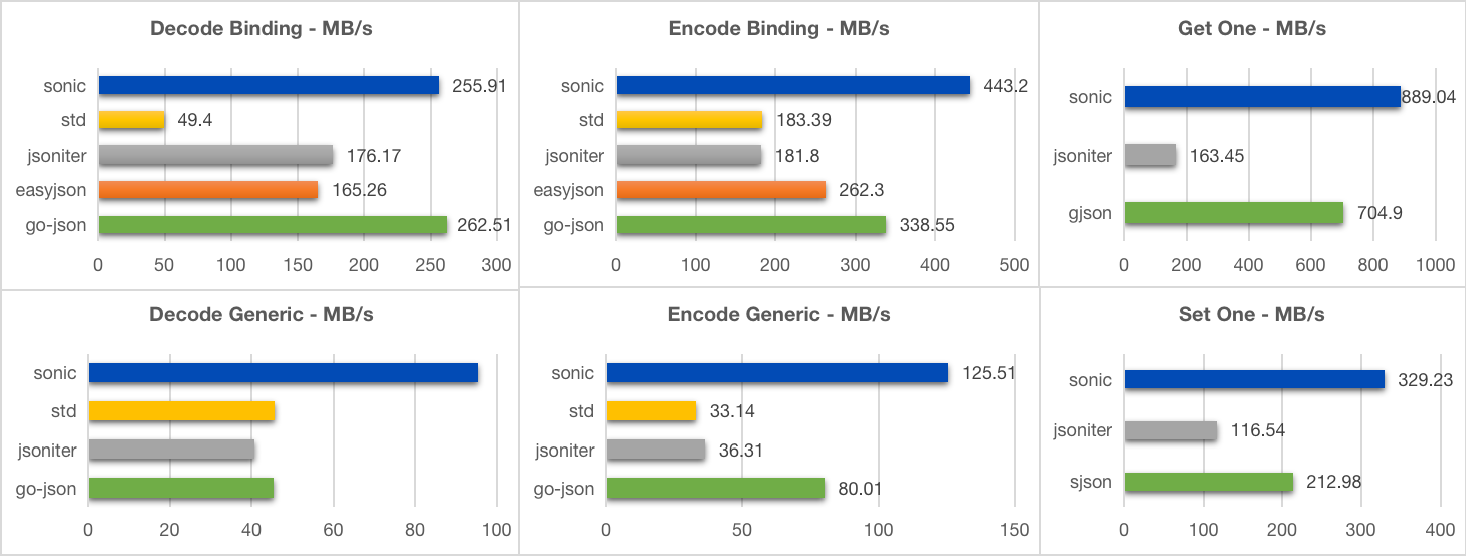
96- [Large](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/testdata/twitter.json) (635KB, 10000+ key, 6 layers)
97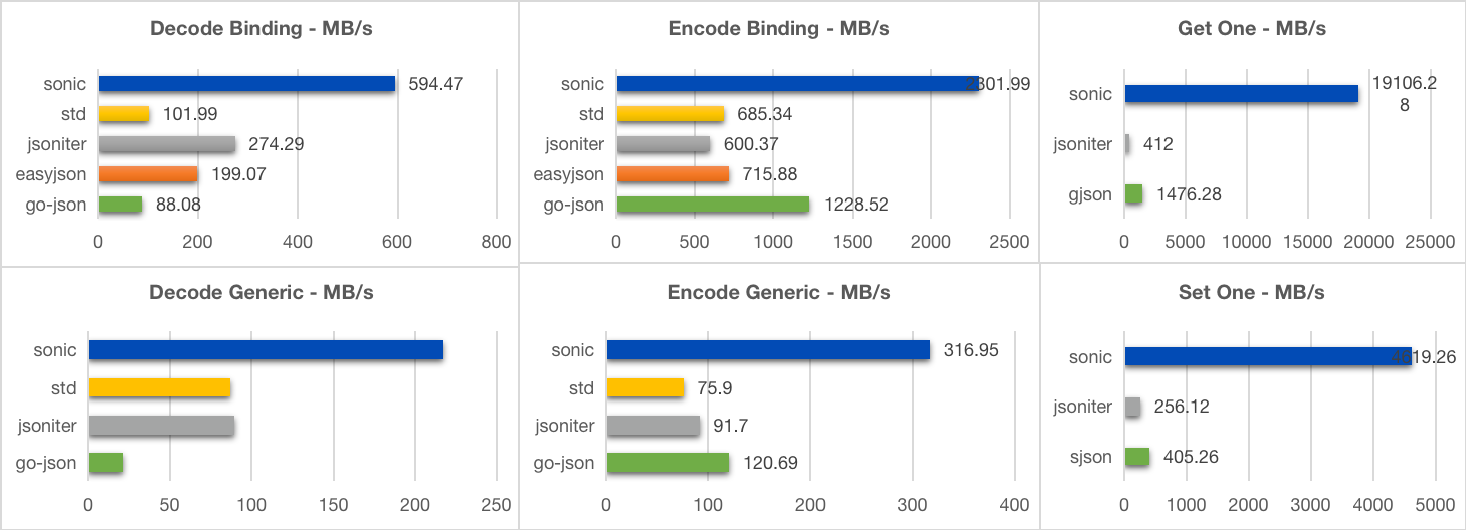
98
99See [bench.sh](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/scripts/bench.sh) for benchmark codes.
100
101## How it works
102
103See [INTRODUCTION.md](./docs/INTRODUCTION.md).
104
105## Usage
106
107### Marshal/Unmarshal
108
109Default behaviors are mostly consistent with `encoding/json`, except HTML escaping form (see [Escape HTML](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/README.md#escape-html)) and `SortKeys` feature (optional support see [Sort Keys](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/README.md#sort-keys)) that is **NOT** in conformity to [RFC8259](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259).
110
111 ```go
112import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
113
114var data YourSchema
115// Marshal
116output, err := sonic.Marshal(&data)
117// Unmarshal
118err := sonic.Unmarshal(output, &data)
119 ```
120
121### Streaming IO
122
123Sonic supports decoding json from `io.Reader` or encoding objects into `io.Writer`, aims at handling multiple values as well as reducing memory consumption.
124
125- encoder
126
127```go
128var o1 = map[string]interface{}{
129 "a": "b",
130}
131var o2 = 1
132var w = bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
133var enc = sonic.ConfigDefault.NewEncoder(w)
134enc.Encode(o1)
135enc.Encode(o2)
136fmt.Println(w.String())
137// Output:
138// {"a":"b"}
139// 1
140```
141
142- decoder
143
144```go
145var o = map[string]interface{}{}
146var r = strings.NewReader(`{"a":"b"}{"1":"2"}`)
147var dec = sonic.ConfigDefault.NewDecoder(r)
148dec.Decode(&o)
149dec.Decode(&o)
150fmt.Printf("%+v", o)
151// Output:
152// map[1:2 a:b]
153```
154
155### Use Number/Use Int64
156
157 ```go
158import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
159
160var input = `1`
161var data interface{}
162
163// default float64
164dc := decoder.NewDecoder(input)
165dc.Decode(&data) // data == float64(1)
166// use json.Number
167dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
168dc.UseNumber()
169dc.Decode(&data) // data == json.Number("1")
170// use int64
171dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
172dc.UseInt64()
173dc.Decode(&data) // data == int64(1)
174
175root, err := sonic.GetFromString(input)
176// Get json.Number
177jn := root.Number()
178jm := root.InterfaceUseNumber().(json.Number) // jn == jm
179// Get float64
180fn := root.Float64()
181fm := root.Interface().(float64) // jn == jm
182 ```
183
184### Sort Keys
185
186On account of the performance loss from sorting (roughly 10%), sonic doesn't enable this feature by default. If your component depends on it to work (like [zstd](https://github.com/facebook/zstd)), Use it like this:
187
188```go
189import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
190import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/encoder"
191
192// Binding map only
193m := map[string]interface{}{}
194v, err := encoder.Encode(m, encoder.SortMapKeys)
195
196// Or ast.Node.SortKeys() before marshal
197var root := sonic.Get(JSON)
198err := root.SortKeys()
199```
200
201### Escape HTML
202
203On account of the performance loss (roughly 15%), sonic doesn't enable this feature by default. You can use `encoder.EscapeHTML` option to open this feature (align with `encoding/json.HTMLEscape`).
204
205```go
206import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
207
208v := map[string]string{"&&":"<>"}
209ret, err := Encode(v, EscapeHTML) // ret == `{"\u0026\u0026":{"X":"\u003c\u003e"}}`
210```
211
212### Compact Format
213
214Sonic encodes primitive objects (struct/map...) as compact-format JSON by default, except marshaling `json.RawMessage` or `json.Marshaler`: sonic ensures validating their output JSON but **DONOT** compacting them for performance concerns. We provide the option `encoder.CompactMarshaler` to add compacting process.
215
216### Print Error
217
218If there invalid syntax in input JSON, sonic will return `decoder.SyntaxError`, which supports pretty-printing of error position
219
220```go
221import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
222import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
223
224var data interface{}
225err := sonic.UnmarshalString("[[[}]]", &data)
226if err != nil {
227 /* One line by default */
228 println(e.Error()) // "Syntax error at index 3: invalid char\n\n\t[[[}]]\n\t...^..\n"
229 /* Pretty print */
230 if e, ok := err.(decoder.SyntaxError); ok {
231 /*Syntax error at index 3: invalid char
232
233 [[[}]]
234 ...^..
235 */
236 print(e.Description())
237 } else if me, ok := err.(*decoder.MismatchTypeError); ok {
238 // decoder.MismatchTypeError is new to Sonic v1.6.0
239 print(me.Description())
240 }
241}
242```
243
244#### Mismatched Types [Sonic v1.6.0]
245
246If there a **mismatch-typed** value for a given key, sonic will report `decoder.MismatchTypeError` (if there are many, report the last one), but still skip wrong the value and keep decoding next JSON.
247
248```go
249import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
250import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
251
252var data = struct{
253 A int
254 B int
255}{}
256err := UnmarshalString(`{"A":"1","B":1}`, &data)
257println(err.Error()) // Mismatch type int with value string "at index 5: mismatched type with value\n\n\t{\"A\":\"1\",\"B\":1}\n\t.....^.........\n"
258fmt.Printf("%+v", data) // {A:0 B:1}
259```
260
261### Ast.Node
262
263Sonic/ast.Node is a completely self-contained AST for JSON. It implements serialization and deserialization both and provides robust APIs for obtaining and modification of generic data.
264
265#### Get/Index
266
267Search partial JSON by given paths, which must be non-negative integer or string, or nil
268
269```go
270import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
271
272input := []byte(`{"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}`)
273
274// no path, returns entire json
275root, err := sonic.Get(input)
276raw := root.Raw() // == string(input)
277
278// multiple paths
279root, err := sonic.Get(input, "key1", 1, "key2")
280sub := root.Get("key3").Index(2).Int64() // == 3
281```
282
283**Tip**: since `Index()` uses offset to locate data, which is much faster than scanning like `Get()`, we suggest you use it as much as possible. And sonic also provides another API `IndexOrGet()` to underlying use offset as well as ensure the key is matched.
284
285#### Set/Unset
286
287Modify the json content by Set()/Unset()
288
289```go
290import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
291
292// Set
293exist, err := root.Set("key4", NewBool(true)) // exist == false
294alias1 := root.Get("key4")
295println(alias1.Valid()) // true
296alias2 := root.Index(1)
297println(alias1 == alias2) // true
298
299// Unset
300exist, err := root.UnsetByIndex(1) // exist == true
301println(root.Get("key4").Check()) // "value not exist"
302```
303
304#### Serialize
305
306To encode `ast.Node` as json, use `MarshalJson()` or `json.Marshal()` (MUST pass the node's pointer)
307
308```go
309import (
310 "encoding/json"
311 "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
312)
313
314buf, err := root.MarshalJson()
315println(string(buf)) // {"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}
316exp, err := json.Marshal(&root) // WARN: use pointer
317println(string(buf) == string(exp)) // true
318```
319
320#### APIs
321
322- validation: `Check()`, `Error()`, `Valid()`, `Exist()`
323- searching: `Index()`, `Get()`, `IndexPair()`, `IndexOrGet()`, `GetByPath()`
324- go-type casting: `Int64()`, `Float64()`, `String()`, `Number()`, `Bool()`, `Map[UseNumber|UseNode]()`, `Array[UseNumber|UseNode]()`, `Interface[UseNumber|UseNode]()`
325- go-type packing: `NewRaw()`, `NewNumber()`, `NewNull()`, `NewBool()`, `NewString()`, `NewObject()`, `NewArray()`
326- iteration: `Values()`, `Properties()`, `ForEach()`, `SortKeys()`
327- modification: `Set()`, `SetByIndex()`, `Add()`
328
329### Ast.Visitor
330
331Sonic provides an advanced API for fully parsing JSON into non-standard types (neither `struct` not `map[string]interface{}`) without using any intermediate representation (`ast.Node` or `interface{}`). For example, you might have the following types which are like `interface{}` but actually not `interface{}`:
332
333```go
334type UserNode interface {}
335
336// the following types implement the UserNode interface.
337type (
338 UserNull struct{}
339 UserBool struct{ Value bool }
340 UserInt64 struct{ Value int64 }
341 UserFloat64 struct{ Value float64 }
342 UserString struct{ Value string }
343 UserObject struct{ Value map[string]UserNode }
344 UserArray struct{ Value []UserNode }
345)
346```
347
348Sonic provides the following API to return **the preorder traversal of a JSON AST**. The `ast.Visitor` is a SAX style interface which is used in some C++ JSON library. You should implement `ast.Visitor` by yourself and pass it to `ast.Preorder()` method. In your visitor you can make your custom types to represent JSON values. There may be an O(n) space container (such as stack) in your visitor to record the object / array hierarchy.
349
350```go
351func Preorder(str string, visitor Visitor, opts *VisitorOptions) error
352
353type Visitor interface {
354 OnNull() error
355 OnBool(v bool) error
356 OnString(v string) error
357 OnInt64(v int64, n json.Number) error
358 OnFloat64(v float64, n json.Number) error
359 OnObjectBegin(capacity int) error
360 OnObjectKey(key string) error
361 OnObjectEnd() error
362 OnArrayBegin(capacity int) error
363 OnArrayEnd() error
364}
365```
366
367See [ast/visitor.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor.go) for detailed usage. We also implement a demo visitor for `UserNode` in [ast/visitor_test.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor_test.go).
368
369## Compatibility
370
371Sonic **DOES NOT** ensure to support all environments, due to the difficulty of developing high-performance codes. For developers who use sonic to build their applications in different environments, we have the following suggestions:
372
373- Developing on **Mac M1**: Make sure you have Rosetta 2 installed on your machine, and set `GOARCH=amd64` when building your application. Rosetta 2 can automatically translate x86 binaries to arm64 binaries and run x86 applications on Mac M1.
374- Developing on **Linux arm64**: You can install qemu and use the `qemu-x86_64 -cpu max` command to convert x86 binaries to amr64 binaries for applications built with sonic. The qemu can achieve a similar transfer effect to Rosetta 2 on Mac M1.
375
376For developers who want to use sonic on Linux arm64 without qemu, or those who want to handle JSON strictly consistent with `encoding/json`, we provide some compatible APIs as `sonic.API`
377
378- `ConfigDefault`: the sonic's default config (`EscapeHTML=false`,`SortKeys=false`...) to run on sonic-supporting environment. It will fall back to `encoding/json` with the corresponding config, and some options like `SortKeys=false` will be invalid.
379- `ConfigStd`: the std-compatible config (`EscapeHTML=true`,`SortKeys=true`...) to run on sonic-supporting environment. It will fall back to `encoding/json`.
380- `ConfigFastest`: the fastest config (`NoQuoteTextMarshaler=true`) to run on sonic-supporting environment. It will fall back to `encoding/json` with the corresponding config, and some options will be invalid.
381
382## Tips
383
384### Pretouch
385
386Since Sonic uses [golang-asm](https://github.com/twitchyliquid64/golang-asm) as a JIT assembler, which is NOT very suitable for runtime compiling, first-hit running of a huge schema may cause request-timeout or even process-OOM. For better stability, we advise **using `Pretouch()` for huge-schema or compact-memory applications** before `Marshal()/Unmarshal()`.
387
388```go
389import (
390 "reflect"
391 "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
392 "github.com/bytedance/sonic/option"
393)
394
395func init() {
396 var v HugeStruct
397
398 // For most large types (nesting depth <= option.DefaultMaxInlineDepth)
399 err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v))
400
401 // with more CompileOption...
402 err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v),
403 // If the type is too deep nesting (nesting depth > option.DefaultMaxInlineDepth),
404 // you can set compile recursive loops in Pretouch for better stability in JIT.
405 option.WithCompileRecursiveDepth(loop),
406 // For a large nested struct, try to set a smaller depth to reduce compiling time.
407 option.WithCompileMaxInlineDepth(depth),
408 )
409}
410```
411
412### Copy string
413
414When decoding **string values without any escaped characters**, sonic references them from the origin JSON buffer instead of mallocing a new buffer to copy. This helps a lot for CPU performance but may leave the whole JSON buffer in memory as long as the decoded objects are being used. In practice, we found the extra memory introduced by referring JSON buffer is usually 20% ~ 80% of decoded objects. Once an application holds these objects for a long time (for example, cache the decoded objects for reusing), its in-use memory on the server may go up. - `Config.CopyString`/`decoder.CopyString()`: We provide the option for `Decode()` / `Unmarshal()` users to choose not to reference the JSON buffer, which may cause a decline in CPU performance to some degree.
415
416- `GetFromStringNoCopy()`: For memory safty, `sonic.Get()` / `sonic.GetFromString()` now copies return JSON. If users want to get json more quickly and not care about memory usage, you can use `GetFromStringNoCopy()` to return a JSON direclty referenced from source.
417
418### Pass string or []byte?
419
420For alignment to `encoding/json`, we provide API to pass `[]byte` as an argument, but the string-to-bytes copy is conducted at the same time considering safety, which may lose performance when the origin JSON is huge. Therefore, you can use `UnmarshalString()` and `GetFromString()` to pass a string, as long as your origin data is a string or **nocopy-cast** is safe for your []byte. We also provide API `MarshalString()` for convenient **nocopy-cast** of encoded JSON []byte, which is safe since sonic's output bytes is always duplicated and unique.
421
422### Accelerate `encoding.TextMarshaler`
423
424To ensure data security, sonic.Encoder quotes and escapes string values from `encoding.TextMarshaler` interfaces by default, which may degrade performance much if most of your data is in form of them. We provide `encoder.NoQuoteTextMarshaler` to skip these operations, which means you **MUST** ensure their output string escaped and quoted following [RFC8259](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259).
425
426### Better performance for generic data
427
428In **fully-parsed** scenario, `Unmarshal()` performs better than `Get()`+`Node.Interface()`. But if you only have a part of the schema for specific json, you can combine `Get()` and `Unmarshal()` together:
429
430```go
431import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
432
433node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
434var user User // your partial schema...
435err = sonic.UnmarshalString(node.Raw(), &user)
436```
437
438Even if you don't have any schema, use `ast.Node` as the container of generic values instead of `map` or `interface`:
439
440```go
441import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
442
443root, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson)
444user := root.GetByPath("statuses", 3, "user") // === root.Get("status").Index(3).Get("user")
445err = user.Check()
446
447// err = user.LoadAll() // only call this when you want to use 'user' concurrently...
448go someFunc(user)
449```
450
451Why? Because `ast.Node` stores its children using `array`:
452
453- `Array`'s performance is **much better** than `Map` when Inserting (Deserialize) and Scanning (Serialize) data;
454- **Hashing** (`map[x]`) is not as efficient as **Indexing** (`array[x]`), which `ast.Node` can conduct on **both array and object**;
455- Using `Interface()`/`Map()` means Sonic must parse all the underlying values, while `ast.Node` can parse them **on demand**.
456
457**CAUTION:** `ast.Node` **DOESN'T** ensure concurrent security directly, due to its **lazy-load** design. However, you can call `Node.Load()`/`Node.LoadAll()` to achieve that, which may bring performance reduction while it still works faster than converting to `map` or `interface{}`
458
459### Ast.Node or Ast.Visitor?
460
461For generic data, `ast.Node` should be enough for your needs in most cases.
462
463However, `ast.Node` is designed for partially processing JSON string. It has some special designs such as lazy-load which might not be suitable for directly parsing the whole JSON string like `Unmarshal()`. Although `ast.Node` is better then `map` or `interface{}`, it's also a kind of intermediate representation after all if your final types are customized and you have to convert the above types to your custom types after parsing.
464
465For better performance, in previous case the `ast.Visitor` will be the better choice. It performs JSON decoding like `Unmarshal()` and you can directly use your final types to represents a JSON AST without any intermediate representations.
466
467But `ast.Visitor` is not a very handy API. You might need to write a lot of code to implement your visitor and carefully maintain the tree hierarchy during decoding. Please read the comments in [ast/visitor.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor.go) carefully if you decide to use this API.
468
469## Community
470
471Sonic is a subproject of [CloudWeGo](https://www.cloudwego.io/). We are committed to building a cloud native ecosystem.
View as plain text