1# Sonic
2
3[English](README.md) | 中文
4
5一个速度奇快的 JSON 序列化/反序列化库,由 JIT (即时编译)和 SIMD (单指令流多数据流)加速。
6
7## 依赖
8
9- Go 1.16~1.22
10- Linux / MacOS / Windows(需要 Go1.17 以上)
11- Amd64 架构
12
13## 接口
14
15详见 [go.dev](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/bytedance/sonic)
16
17## 特色
18
19- 运行时对象绑定,无需代码生成
20- 完备的 JSON 操作 API
21- 快,更快,还要更快!
22
23## 基准测试
24
25对于**所有大小**的 json 和**所有使用场景**, **Sonic 表现均为最佳**。
26
27- [中型](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/decoder/testdata_test.go#L19) (13kB, 300+ 键, 6 层)
28
29```powershell
30goversion: 1.17.1
31goos: darwin
32goarch: amd64
33cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-9880H CPU @ 2.30GHz
34BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic-16 32393 ns/op 402.40 MB/s 11965 B/op 4 allocs/op
35BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 21668 ns/op 601.57 MB/s 10940 B/op 4 allocs/op
36BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 42168 ns/op 309.12 MB/s 14345 B/op 115 allocs/op
37BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_GoJson-16 65189 ns/op 199.96 MB/s 23261 B/op 16 allocs/op
38BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_StdLib-16 106322 ns/op 122.60 MB/s 49136 B/op 789 allocs/op
39BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic-16 6269 ns/op 2079.26 MB/s 14173 B/op 4 allocs/op
40BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 5281 ns/op 2468.16 MB/s 12322 B/op 4 allocs/op
41BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 20056 ns/op 649.93 MB/s 9488 B/op 2 allocs/op
42BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_GoJson-16 8311 ns/op 1568.32 MB/s 9481 B/op 1 allocs/op
43BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_StdLib-16 16448 ns/op 792.52 MB/s 9479 B/op 1 allocs/op
44BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 6681 ns/op 1950.93 MB/s 12738 B/op 4 allocs/op
45BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 4179 ns/op 3118.99 MB/s 10757 B/op 4 allocs/op
46BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 9861 ns/op 1321.84 MB/s 14362 B/op 115 allocs/op
47BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 18850 ns/op 691.52 MB/s 23278 B/op 16 allocs/op
48BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 45902 ns/op 283.97 MB/s 49174 B/op 789 allocs/op
49BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 1480 ns/op 8810.09 MB/s 13049 B/op 4 allocs/op
50BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 1209 ns/op 10785.23 MB/s 11546 B/op 4 allocs/op
51BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 6170 ns/op 2112.58 MB/s 9504 B/op 2 allocs/op
52BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 3321 ns/op 3925.52 MB/s 9496 B/op 1 allocs/op
53BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 3739 ns/op 3486.49 MB/s 9480 B/op 1 allocs/op
54
55BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic-16 66812 ns/op 195.10 MB/s 57602 B/op 723 allocs/op
56BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 54523 ns/op 239.07 MB/s 49786 B/op 313 allocs/op
57BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_StdLib-16 124260 ns/op 104.90 MB/s 50869 B/op 772 allocs/op
58BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 91274 ns/op 142.81 MB/s 55782 B/op 1068 allocs/op
59BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_GoJson-16 88569 ns/op 147.17 MB/s 66367 B/op 973 allocs/op
60BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic-16 32557 ns/op 400.38 MB/s 28302 B/op 137 allocs/op
61BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 28649 ns/op 455.00 MB/s 24999 B/op 34 allocs/op
62BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_StdLib-16 111437 ns/op 116.97 MB/s 10576 B/op 208 allocs/op
63BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 35090 ns/op 371.48 MB/s 14673 B/op 385 allocs/op
64BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_GoJson-16 28738 ns/op 453.59 MB/s 22039 B/op 49 allocs/op
65BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 12321 ns/op 1057.91 MB/s 57233 B/op 723 allocs/op
66BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic_Fast-16 10644 ns/op 1224.64 MB/s 49362 B/op 313 allocs/op
67BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 57587 ns/op 226.35 MB/s 50874 B/op 772 allocs/op
68BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 38666 ns/op 337.12 MB/s 55789 B/op 1068 allocs/op
69BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_GoJson-16 30259 ns/op 430.79 MB/s 66370 B/op 974 allocs/op
70BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 5965 ns/op 2185.28 MB/s 27747 B/op 137 allocs/op
71BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic_Fast-16 5170 ns/op 2521.31 MB/s 24715 B/op 34 allocs/op
72BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 27582 ns/op 472.58 MB/s 10576 B/op 208 allocs/op
73BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 13571 ns/op 960.51 MB/s 14685 B/op 385 allocs/op
74BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_GoJson-16 10031 ns/op 1299.51 MB/s 22111 B/op 49 allocs/op
75
76BenchmarkGetOne_Sonic-16 3276 ns/op 3975.78 MB/s 24 B/op 1 allocs/op
77BenchmarkGetOne_Gjson-16 9431 ns/op 1380.81 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
78BenchmarkGetOne_Jsoniter-16 51178 ns/op 254.46 MB/s 27936 B/op 647 allocs/op
79BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 216.7 ns/op 60098.95 MB/s 24 B/op 1 allocs/op
80BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Gjson-16 1076 ns/op 12098.62 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
81BenchmarkGetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 17741 ns/op 734.06 MB/s 27945 B/op 647 allocs/op
82BenchmarkSetOne_Sonic-16 9571 ns/op 1360.61 MB/s 1584 B/op 17 allocs/op
83BenchmarkSetOne_Sjson-16 36456 ns/op 357.22 MB/s 52180 B/op 9 allocs/op
84BenchmarkSetOne_Jsoniter-16 79475 ns/op 163.86 MB/s 45862 B/op 964 allocs/op
85BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 850.9 ns/op 15305.31 MB/s 1584 B/op 17 allocs/op
86BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Sjson-16 18194 ns/op 715.77 MB/s 52247 B/op 9 allocs/op
87BenchmarkSetOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 33560 ns/op 388.05 MB/s 45892 B/op 964 allocs/op
88BenchmarkLoadNode/LoadAll()-16 11384 ns/op 1143.93 MB/s 6307 B/op 25 allocs/op
89BenchmarkLoadNode_Parallel/LoadAll()-16 5493 ns/op 2370.68 MB/s 7145 B/op 25 allocs/op
90BenchmarkLoadNode/Interface()-16 17722 ns/op 734.85 MB/s 13323 B/op 88 allocs/op
91BenchmarkLoadNode_Parallel/Interface()-16 10330 ns/op 1260.70 MB/s 15178 B/op 88 allocs/op
92```
93
94- [小型](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/testdata/small.go) (400B, 11 个键, 3 层)
95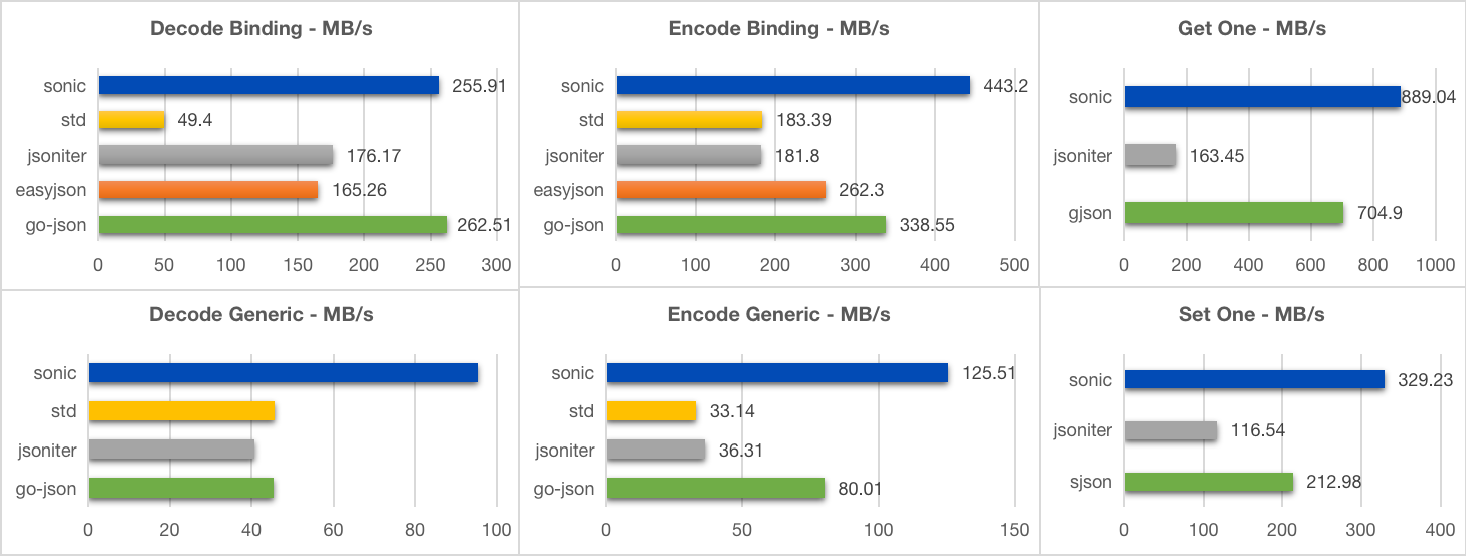
96- [大型](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/testdata/twitter.json) (635kB, 10000+ 个键, 6 层)
97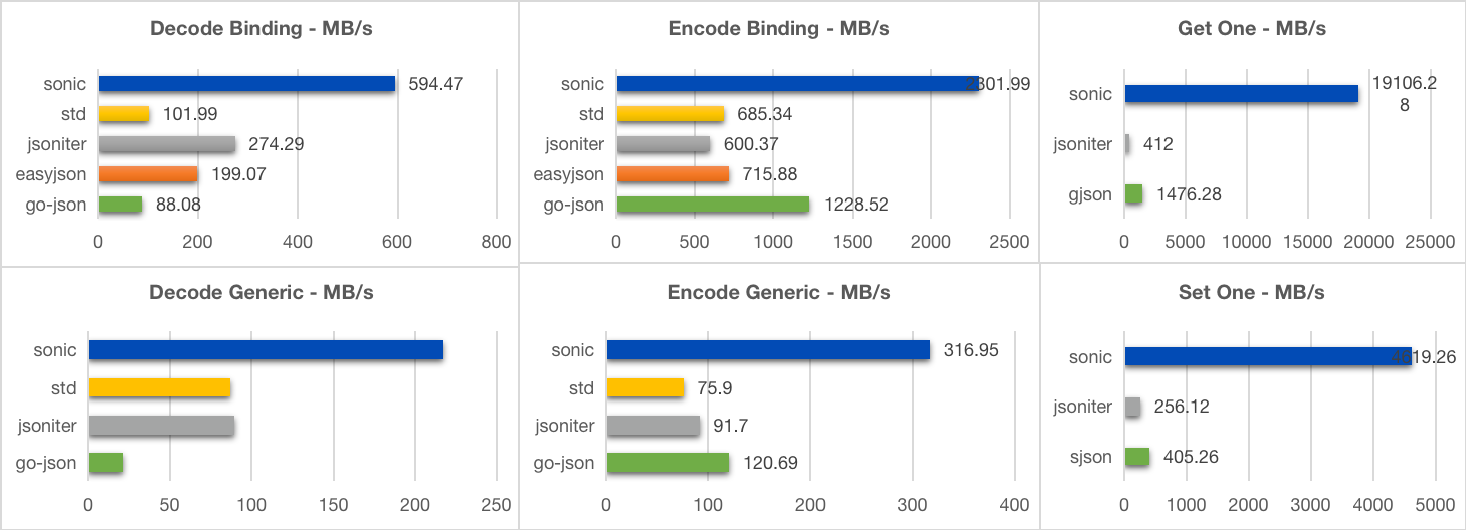
98
99要查看基准测试代码,请参阅 [bench.sh](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/scripts/bench.sh) 。
100
101## 工作原理
102
103请参阅 [INTRODUCTION_ZH_CN.md](./docs/INTRODUCTION_ZH_CN.md).
104
105## 使用方式
106
107### 序列化/反序列化
108
109默认的行为基本上与 `encoding/json` 相一致,除了 HTML 转义形式(参见 [Escape HTML](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/README.md#escape-html)) 和 `SortKeys` 功能(参见 [Sort Keys](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/README.md#sort-keys))**没有**遵循 [RFC8259](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259) 。
110
111 ```go
112import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
113
114var data YourSchema
115// Marshal
116output, err := sonic.Marshal(&data)
117// Unmarshal
118err := sonic.Unmarshal(output, &data)
119 ```
120
121### 流式输入输出
122
123Sonic 支持解码 `io.Reader` 中输入的 json,或将对象编码为 json 后输出至 `io.Writer`,以处理多个值并减少内存消耗。
124
125- 编码器
126
127```go
128var o1 = map[string]interface{}{
129 "a": "b",
130}
131var o2 = 1
132var w = bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
133var enc = sonic.ConfigDefault.NewEncoder(w)
134enc.Encode(o1)
135enc.Encode(o2)
136fmt.Println(w.String())
137// Output:
138// {"a":"b"}
139// 1
140```
141
142- 解码器
143
144```go
145var o = map[string]interface{}{}
146var r = strings.NewReader(`{"a":"b"}{"1":"2"}`)
147var dec = sonic.ConfigDefault.NewDecoder(r)
148dec.Decode(&o)
149dec.Decode(&o)
150fmt.Printf("%+v", o)
151// Output:
152// map[1:2 a:b]
153```
154
155### 使用 `Number` / `int64`
156
157```go
158import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
159
160var input = `1`
161var data interface{}
162
163// default float64
164dc := decoder.NewDecoder(input)
165dc.Decode(&data) // data == float64(1)
166// use json.Number
167dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
168dc.UseNumber()
169dc.Decode(&data) // data == json.Number("1")
170// use int64
171dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
172dc.UseInt64()
173dc.Decode(&data) // data == int64(1)
174
175root, err := sonic.GetFromString(input)
176// Get json.Number
177jn := root.Number()
178jm := root.InterfaceUseNumber().(json.Number) // jn == jm
179// Get float64
180fn := root.Float64()
181fm := root.Interface().(float64) // jn == jm
182 ```
183
184### 对键排序
185
186考虑到排序带来的性能损失(约 10% ), sonic 默认不会启用这个功能。如果你的组件依赖这个行为(如 [zstd](https://github.com/facebook/zstd)) ,可以仿照下面的例子:
187
188```go
189import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
190import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/encoder"
191
192// Binding map only
193m := map[string]interface{}{}
194v, err := encoder.Encode(m, encoder.SortMapKeys)
195
196// Or ast.Node.SortKeys() before marshal
197var root := sonic.Get(JSON)
198err := root.SortKeys()
199```
200
201### HTML 转义
202
203考虑到性能损失(约15%), sonic 默认不会启用这个功能。你可以使用 `encoder.EscapeHTML` 选项来开启(与 `encoding/json.HTMLEscape` 行为一致)。
204
205```go
206import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
207
208v := map[string]string{"&&":"<>"}
209ret, err := Encode(v, EscapeHTML) // ret == `{"\u0026\u0026":{"X":"\u003c\u003e"}}`
210```
211
212### 紧凑格式
213
214Sonic 默认将基本类型( `struct` , `map` 等)编码为紧凑格式的 JSON ,除非使用 `json.RawMessage` or `json.Marshaler` 进行编码: sonic 确保输出的 JSON 合法,但出于性能考虑,**不会**加工成紧凑格式。我们提供选项 `encoder.CompactMarshaler` 来添加此过程,
215
216### 打印错误
217
218如果输入的 JSON 存在无效的语法,sonic 将返回 `decoder.SyntaxError`,该错误支持错误位置的美化输出。
219
220```go
221import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
222import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
223
224var data interface{}
225err := sonic.UnmarshalString("[[[}]]", &data)
226if err != nil {
227 /* One line by default */
228 println(e.Error()) // "Syntax error at index 3: invalid char\n\n\t[[[}]]\n\t...^..\n"
229 /* Pretty print */
230 if e, ok := err.(decoder.SyntaxError); ok {
231 /*Syntax error at index 3: invalid char
232
233 [[[}]]
234 ...^..
235 */
236 print(e.Description())
237 } else if me, ok := err.(*decoder.MismatchTypeError); ok {
238 // decoder.MismatchTypeError is new to Sonic v1.6.0
239 print(me.Description())
240 }
241}
242```
243
244#### 类型不匹配 [Sonic v1.6.0]
245
246如果给定键中存在**类型不匹配**的值, sonic 会抛出 `decoder.MismatchTypeError` (如果有多个,只会报告最后一个),但仍会跳过错误的值并解码下一个 JSON 。
247
248```go
249import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
250import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
251
252var data = struct{
253 A int
254 B int
255}{}
256err := UnmarshalString(`{"A":"1","B":1}`, &data)
257println(err.Error()) // Mismatch type int with value string "at index 5: mismatched type with value\n\n\t{\"A\":\"1\",\"B\":1}\n\t.....^.........\n"
258fmt.Printf("%+v", data) // {A:0 B:1}
259```
260
261### `Ast.Node`
262
263Sonic/ast.Node 是完全独立的 JSON 抽象语法树库。它实现了序列化和反序列化,并提供了获取和修改通用数据的鲁棒的 API。
264
265#### 查找/索引
266
267通过给定的路径搜索 JSON 片段,路径必须为非负整数,字符串或 `nil` 。
268
269```go
270import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
271
272input := []byte(`{"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}`)
273
274// no path, returns entire json
275root, err := sonic.Get(input)
276raw := root.Raw() // == string(input)
277
278// multiple paths
279root, err := sonic.Get(input, "key1", 1, "key2")
280sub := root.Get("key3").Index(2).Int64() // == 3
281```
282
283**注意**:由于 `Index()` 使用偏移量来定位数据,比使用扫描的 `Get()` 要快的多,建议尽可能的使用 `Index` 。 Sonic 也提供了另一个 API, `IndexOrGet()` ,以偏移量为基础并且也确保键的匹配。
284
285#### 修改
286
287使用 `Set()` / `Unset()` 修改 json 的内容
288
289```go
290import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
291
292// Set
293exist, err := root.Set("key4", NewBool(true)) // exist == false
294alias1 := root.Get("key4")
295println(alias1.Valid()) // true
296alias2 := root.Index(1)
297println(alias1 == alias2) // true
298
299// Unset
300exist, err := root.UnsetByIndex(1) // exist == true
301println(root.Get("key4").Check()) // "value not exist"
302```
303
304#### 序列化
305
306要将 `ast.Node` 编码为 json ,使用 `MarshalJson()` 或者 `json.Marshal()` (必须传递指向节点的指针)
307
308```go
309import (
310 "encoding/json"
311 "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
312)
313
314buf, err := root.MarshalJson()
315println(string(buf)) // {"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}
316exp, err := json.Marshal(&root) // WARN: use pointer
317println(string(buf) == string(exp)) // true
318```
319
320#### APIs
321
322- 合法性检查: `Check()`, `Error()`, `Valid()`, `Exist()`
323- 索引: `Index()`, `Get()`, `IndexPair()`, `IndexOrGet()`, `GetByPath()`
324- 转换至 go 内置类型: `Int64()`, `Float64()`, `String()`, `Number()`, `Bool()`, `Map[UseNumber|UseNode]()`, `Array[UseNumber|UseNode]()`, `Interface[UseNumber|UseNode]()`
325- go 类型打包: `NewRaw()`, `NewNumber()`, `NewNull()`, `NewBool()`, `NewString()`, `NewObject()`, `NewArray()`
326- 迭代: `Values()`, `Properties()`, `ForEach()`, `SortKeys()`
327- 修改: `Set()`, `SetByIndex()`, `Add()`
328
329### `Ast.Visitor`
330
331Sonic 提供了一个高级的 API 用于直接全量解析 JSON 到非标准容器里 (既不是 `struct` 也不是 `map[string]interface{}`) 且不需要借助任何中间表示 (`ast.Node` 或 `interface{}`)。举个例子,你可能定义了下述的类型,它们看起来像 `interface{}`,但实际上并不是:
332
333```go
334type UserNode interface {}
335
336// the following types implement the UserNode interface.
337type (
338 UserNull struct{}
339 UserBool struct{ Value bool }
340 UserInt64 struct{ Value int64 }
341 UserFloat64 struct{ Value float64 }
342 UserString struct{ Value string }
343 UserObject struct{ Value map[string]UserNode }
344 UserArray struct{ Value []UserNode }
345)
346```
347
348Sonic 提供了下述的 API 来返回 **“对 JSON AST 的前序遍历”**。`ast.Visitor` 是一个 SAX 风格的接口,这在某些 C++ 的 JSON 解析库中被使用到。你需要自己实现一个 `ast.Visitor`,将它传递给 `ast.Preorder()` 方法。在你的实现中你可以使用自定义的类型来表示 JSON 的值。在你的 `ast.Visitor` 中,可能需要有一个 O(n) 空间复杂度的容器(比如说栈)来记录 object / array 的层级。
349
350```go
351func Preorder(str string, visitor Visitor, opts *VisitorOptions) error
352
353type Visitor interface {
354 OnNull() error
355 OnBool(v bool) error
356 OnString(v string) error
357 OnInt64(v int64, n json.Number) error
358 OnFloat64(v float64, n json.Number) error
359 OnObjectBegin(capacity int) error
360 OnObjectKey(key string) error
361 OnObjectEnd() error
362 OnArrayBegin(capacity int) error
363 OnArrayEnd() error
364}
365```
366
367详细用法参看 [ast/visitor.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor.go),我们还为 `UserNode` 实现了一个示例 `ast.Visitor`,你可以在 [ast/visitor_test.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor_test.go) 中找到它。
368
369## 兼容性
370
371由于开发高性能代码的困难性, Sonic **不**保证对所有环境的支持。对于在不同环境中使用 Sonic 构建应用程序的开发者,我们有以下建议:
372
373- 在 **Mac M1** 上开发:确保在您的计算机上安装了 Rosetta 2,并在构建时设置 `GOARCH=amd64` 。 Rosetta 2 可以自动将 x86 二进制文件转换为 arm64 二进制文件,并在 Mac M1 上运行 x86 应用程序。
374- 在 **Linux arm64** 上开发:您可以安装 qemu 并使用 `qemu-x86_64 -cpu max` 命令来将 x86 二进制文件转换为 arm64 二进制文件。qemu可以实现与Mac M1上的Rosetta 2类似的转换效果。
375
376对于希望在不使用 qemu 下使用 sonic 的开发者,或者希望处理 JSON 时与 `encoding/JSON` 严格保持一致的开发者,我们在 `sonic.API` 中提供了一些兼容性 API
377
378- `ConfigDefault`: 在支持 sonic 的环境下 sonic 的默认配置(`EscapeHTML=false`,`SortKeys=false`等)。行为与具有相应配置的 `encoding/json` 一致,一些选项,如 `SortKeys=false` 将无效。
379- `ConfigStd`: 在支持 sonic 的环境下与标准库兼容的配置(`EscapeHTML=true`,`SortKeys=true`等)。行为与 `encoding/json` 一致。
380- `ConfigFastest`: 在支持 sonic 的环境下运行最快的配置(`NoQuoteTextMarshaler=true`)。行为与具有相应配置的 `encoding/json` 一致,某些选项将无效。
381
382## 注意事项
383
384### 预热
385
386由于 Sonic 使用 [golang-asm](https://github.com/twitchyliquid64/golang-asm) 作为 JIT 汇编器,这个库并不适用于运行时编译,第一次运行一个大型模式可能会导致请求超时甚至进程内存溢出。为了更好地稳定性,我们建议在运行大型模式或在内存有限的应用中,在使用 `Marshal()/Unmarshal()` 前运行 `Pretouch()`。
387
388```go
389import (
390 "reflect"
391 "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
392 "github.com/bytedance/sonic/option"
393)
394
395func init() {
396 var v HugeStruct
397
398 // For most large types (nesting depth <= option.DefaultMaxInlineDepth)
399 err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v))
400
401 // with more CompileOption...
402 err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v),
403 // If the type is too deep nesting (nesting depth > option.DefaultMaxInlineDepth),
404 // you can set compile recursive loops in Pretouch for better stability in JIT.
405 option.WithCompileRecursiveDepth(loop),
406 // For a large nested struct, try to set a smaller depth to reduce compiling time.
407 option.WithCompileMaxInlineDepth(depth),
408 )
409}
410```
411
412### 拷贝字符串
413
414当解码 **没有转义字符的字符串**时, sonic 会从原始的 JSON 缓冲区内引用而不是复制到新的一个缓冲区中。这对 CPU 的性能方面很有帮助,但是可能因此在解码后对象仍在使用的时候将整个 JSON 缓冲区保留在内存中。实践中我们发现,通过引用 JSON 缓冲区引入的额外内存通常是解码后对象的 20% 至 80% ,一旦应用长期保留这些对象(如缓存以备重用),服务器所使用的内存可能会增加。我们提供了选项 `decoder.CopyString()` 供用户选择,不引用 JSON 缓冲区。这可能在一定程度上降低 CPU 性能。
415
416### 传递字符串还是字节数组?
417
418为了和 `encoding/json` 保持一致,我们提供了传递 `[]byte` 作为参数的 API ,但考虑到安全性,字符串到字节的复制是同时进行的,这在原始 JSON 非常大时可能会导致性能损失。因此,你可以使用 `UnmarshalString()` 和 `GetFromString()` 来传递字符串,只要你的原始数据是字符串,或**零拷贝类型转换**对于你的字节数组是安全的。我们也提供了 `MarshalString()` 的 API ,以便对编码的 JSON 字节数组进行**零拷贝类型转换**,因为 sonic 输出的字节始终是重复并且唯一的,所以这样是安全的。
419
420### 加速 `encoding.TextMarshaler`
421
422为了保证数据安全性, `sonic.Encoder` 默认会对来自 `encoding.TextMarshaler` 接口的字符串进行引用和转义,如果大部分数据都是这种形式那可能会导致很大的性能损失。我们提供了 `encoder.NoQuoteTextMarshaler` 选项来跳过这些操作,但你**必须**保证他们的输出字符串依照 [RFC8259](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259) 进行了转义和引用。
423
424### 泛型的性能优化
425
426在 **完全解析**的场景下, `Unmarshal()` 表现得比 `Get()`+`Node.Interface()` 更好。但是如果你只有特定 JSON 的部分模式,你可以将 `Get()` 和 `Unmarshal()` 结合使用:
427
428```go
429import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
430
431node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
432var user User // your partial schema...
433err = sonic.UnmarshalString(node.Raw(), &user)
434```
435
436甚至如果你没有任何模式,可以用 `ast.Node` 代替 `map` 或 `interface` 作为泛型的容器:
437
438```go
439import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
440
441root, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson)
442user := root.GetByPath("statuses", 3, "user") // === root.Get("status").Index(3).Get("user")
443err = user.Check()
444
445// err = user.LoadAll() // only call this when you want to use 'user' concurrently...
446go someFunc(user)
447```
448
449为什么?因为 `ast.Node` 使用 `array` 来存储其子节点:
450
451- 在插入(反序列化)和扫描(序列化)数据时,`Array` 的性能比 `Map` **好得多**;
452- **哈希**(`map[x]`)的效率不如**索引**(`array[x]`)高效,而 `ast.Node` 可以在数组和对象上使用索引;
453- 使用 `Interface()` / `Map()` 意味着 sonic 必须解析所有的底层值,而 `ast.Node` 可以**按需解析**它们。
454
455**注意**:由于 `ast.Node` 的惰性加载设计,其**不能**直接保证并发安全性,但你可以调用 `Node.Load()` / `Node.LoadAll()` 来实现并发安全。尽管可能会带来性能损失,但仍比转换成 `map` 或 `interface{}` 更为高效。
456
457### 使用 `ast.Node` 还是 `ast.Visitor`?
458
459对于泛型数据的解析,`ast.Node` 在大多数场景上应该能够满足你的需求。
460
461然而,`ast.Node` 是一种针对部分解析 JSON 而设计的泛型容器,它包含一些特殊设计,比如惰性加载,如果你希望像 `Unmarshal()` 那样直接解析整个 JSON,这些设计可能并不合适。尽管 `ast.Node` 相较于 `map` 或 `interface{}` 来说是更好的一种泛型容器,但它毕竟也是一种中间表示,如果你的最终类型是自定义的,你还得在解析完成后将上述类型转化成你自定义的类型。
462
463在上述场景中,如果想要有更极致的性能,`ast.Visitor` 会是更好的选择。它采用和 `Unmarshal()` 类似的形式解析 JSON,并且你可以直接使用你的最终类型去表示 JSON AST,而不需要经过额外的任何中间表示。
464
465但是,`ast.Visitor` 并不是一个很易用的 API。你可能需要写大量的代码去实现自己的 `ast.Visitor`,并且需要在解析过程中仔细维护树的层级。如果你决定要使用这个 API,请先仔细阅读 [ast/visitor.go](https://github.com/bytedance/sonic/blob/main/ast/visitor.go) 中的注释。
466
467## 社区
468
469Sonic 是 [CloudWeGo](https://www.cloudwego.io/) 下的一个子项目。我们致力于构建云原生生态系统。
View as plain text